So What Is rDNA?
That's a very good question! rDNA stands for recombinant DNA. Before
we get to the "r" part, we need to understand DNA. Those of you with
a background in biology probably know about DNA, but a lot of ChemE's haven't
seen DNA since high school biology. DNA is the keeper of the all the information
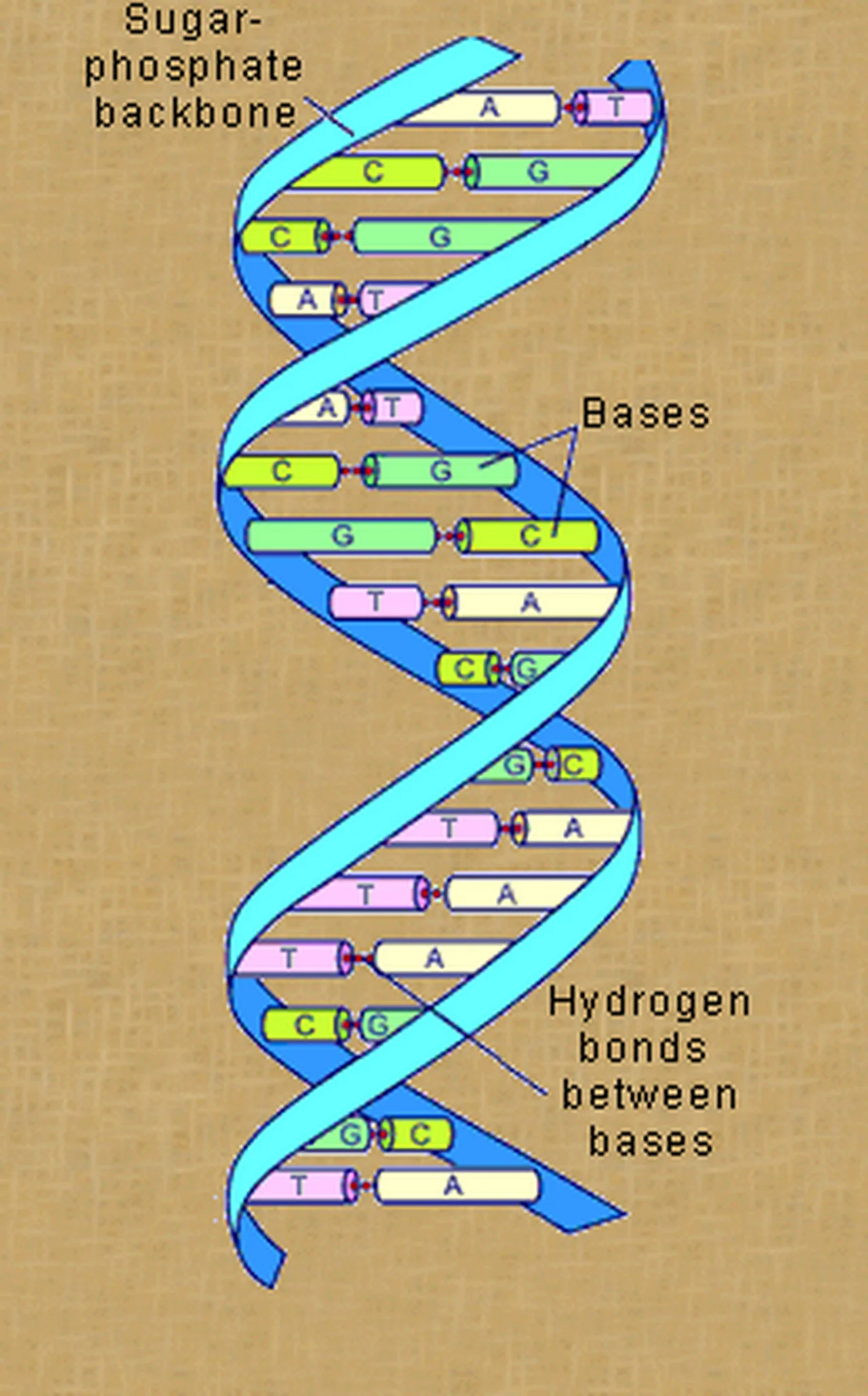
needed to recreate an organism. All DNA is made up of a base consisting
of sugar, phosphate and one nitrogen base. There are four nitrogen bases,
adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). The nitrogen
bases are found in pairs, with A & T and G & C paired together. The sequence
of the nitrogen bases can be arranged in an infinite ways, and their structure is known as
the famous "double helix" which is shown in the image below. The sugar used in
DNA is deoxyribose. The four nitrogen bases are the same for all organisms. The
sequence and number of bases is what creates diversity. DNA does not
actually make the organism, it only makes proteins. The DNA is transcribed
into mRNA and mRNA is translated into protein, and the protein then forms the
organism. By changing the DNA sequence, the way in which the protein is
formed changes. This leads to either a different protein, or an inactive protein.
Read Further:
https://www.rpi.edu/dept/chem-eng/Biotech-Environ/Projects00/rdna/rdna.html